The Muscular System and Digestive System in Human
Maharashtra Board General Science Chapter 12
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn:
|
Organ system : The group of organs performing similar functions together in a body is called an ‘organ system’.
Muscular system : Muscles are bundles of fibres that can contract and relax as required.
- The fleshy part on the bones are muscles.
- Due to contraction and relaxation of the muscles body parts are able to move. Muscles give our body a specific shape and posture.
- They are in the form of bundles of fibres.
Muscles are firmly attached to bones by means of tendons. Due to contraction and relaxation of muscles, the bones are able to move. This helps in movement of our body. Bones are joined to each other by ligaments.
- Myology is the study of muscles.
- Thigh muscle is the largest muscle in our body.
- The smallest muscle is attached to stapes. (A bone in the ear).
Movements of muscles :
- Muscles are firmly attached to bones by means of tendons.
- Due to contraction of muscles, there is movement at the joint. This induces movements in the bones. They move either nearer to or away from each other.
- All kinds of movements are because of the action of muscles. Various movements like talking, laughing, walking, jumping, throwing, movements of eyelids etc. are possible due to muscles.
- Muscles are present in all the parts of the body. As the body growth takes place, the muscles also grow.
- About 600 muscles are present in the human body. They contribute almost 40% of the body weight. About 30 muscles are present in the human face. They help in showing expressions.
Types of muscles (According to the functions) :
- Voluntary muscles : The muscles that Work under our will are called voluntary muscles. e.g. muscles that help in the movements of hands and legs.
- Involuntary muscles : The muscles that do not work under our will are called involuntary muscles. Some vital processes like breathing, blood circulation, digestion are essential for life. They are not under our control or will. e.g. muscles of Stomach, intestine etc. are involuntary muscles.
Types of muscles (According to structure) :
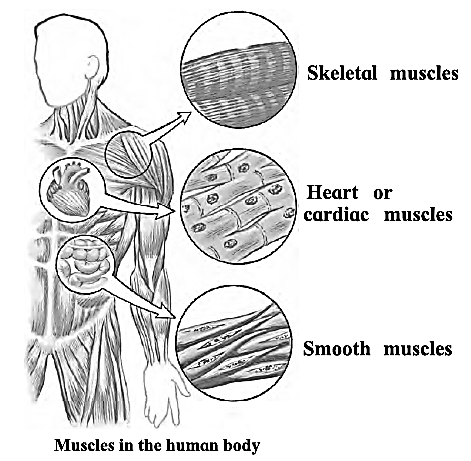
(1) Skeletal muscles : The muscles which are attached to the skeleton and those which hold the bones are called skeletal muscles. They also give shape to our body. They are voluntary in function. The two ends of skeletal muscles are attached to two different bones. e.g. Muscles of the arms and legs.
(2) Heart or cardiac muscles : These muscles form the heart wall and they bring about continuous contraction and relaxation of the heart. This is known as beating of heart which is involuntary. In one minute, heart beats about 70 times.
(3) Smooth muscles : These are involuntary muscles which are present in the internal vital organs other than the heart. e.g., muscles of the stomach, intestine, blood vessels, uterus, etc. are called smooth muscles. They carry out many vital functions of our body such as breathing, movement of alimentary canal etc.
Functions of muscles :
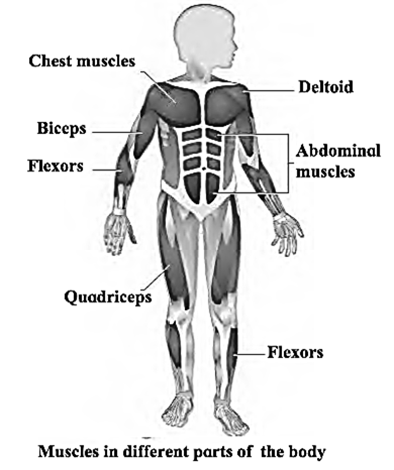
- For the body movements, the muscles always work in groups .When some muscles undergo contraction, other muscles of the same group show relaxation.
- With this alternating action, the muscles Work in coordination to perform various functions of our body.
- Biceps : The muscle in the front of the bone of upper arm.
- Triceps : The muscle at the back of the bone of upper arm.
Care of muscles :
- The muscles should be kept strong and efficient.
- This is possible due to diet that includes proteins and carbohydrates. This helps in the proper growth and repair of muscles.
- Regular exercise keeps the muscles fit and strong.
- We should keep our posture and gait proper. Sitting with a straight back, is essential. With hunch back, there are changes in the structure of the vertebrae causing disorders of vertebral column. Shoulder and back muscles start hurting. Disorders of the vertebral column may also arise.
- Due to exercise, movements of the heart muscles and breathing rises causing increased oxygen and nutrient supply to the entire body.
Digestive system : The food that is taken inside the body is completely digested in the alimentary canal. The nutrients obtained through the digestion are absorbed in the blood.
Digestion of food : Converting the food into a soluble form and then absorbing it in to the blood is called digestion.
The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and digestive glands.
- Parts of the alimentary canal : Mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, rectum and anal.
- Digestive glands : The salivary glands, liver and pancreas.
- Length of alimentary canal : About 9 metres.
Each organ of the digestive system systematically perform the function of digestion
Structure and function of Digestive organs :
Teeth :
- Functions of teeth : Helps in chewing the food and making it into particulate form. The food then mixes with saliva and is easier to swallow.
- Types of teeth : Four types of teeth : Incisors, Canines, Pre-molars and Molars.
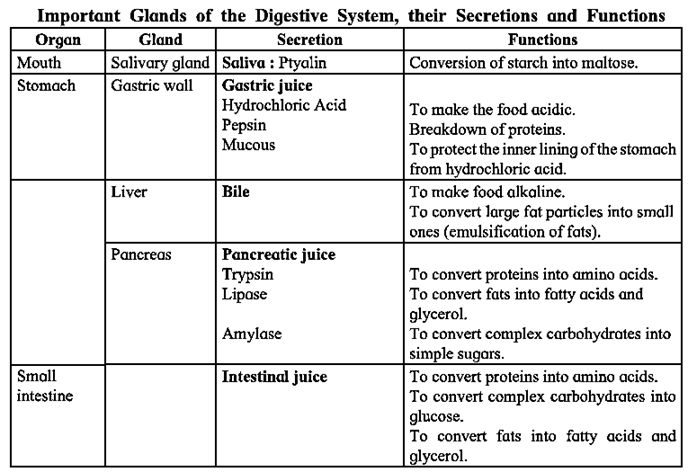
- Each type has specific function. Calcium salts make the enamel of each tooth. The food in mouth is mixed with saliva and is easier for gulping. Saliva has an enzyme called ptyalin or salivary amylase which converts starch into a maltose.
Enzymes : Enzymes are catalyst chemicals produced in the body to bring about specific chemical reactions. Digestive enzymes bring about metabolic processes. Enzymes are active at normal body temperature.
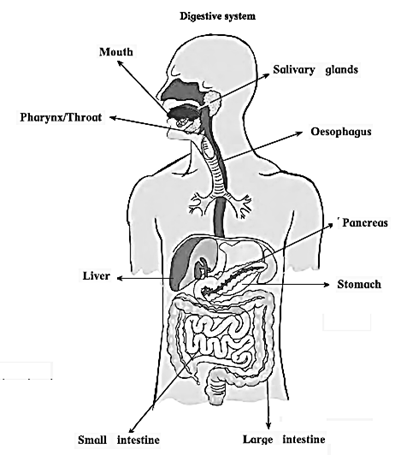
Mouth : Digestion of food starts with the help of salivary amylase in the mouth.
Food is chewed with the help of teeth and tasted with tongue. After chewing and mixing with saliva it is gulped.
Pharynx : The food pipe (oesophagus) and the wind pipe (trachea) both open into the pharynx. A small flap called epiglottis guard the opening of trachea while gulping the food.
Oesophagus : The tube taking the food from pharynx to the stomach.
Stomach : The widest sac like part the alimentary canal. It has gastric glands that secrete gastric juice. It contains hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus.
Food is churned and made acidic in stomach. Some proteins are digested here.
Churning and the action of gastric juice makes slurry from food which then goes in the small intestine.
Small intestine : The long tube of 6m length. Three different digestive juices are mixed with the acidic food that comes from stomach. Completion of digestion and absorption of nutrients into the blood takes place here.
Large intestine : The wide tubular 1.5m long large intestine absorbs only water.
There is functionless ‘appendix’ is attached to the first part of large intestine.
Undigested matter is stored for some time and then thrown out of the body through anus.
Digestive glands :
- Liver : Largest gland in the body. Has lot of blood supply. Main function is storage of glucose. Liver secrets bile juice which is stored in the gall bladder. Bile juice helps in digestion of fats.
- Pancreas : It secretes the pancreatic juice.
- Salivary glands : There are three pairs of salivary glands. One pair near the ear, one pair in the pharynx and one pair below the tongue. They secrete saliva contains ptyalin or salivary amylase.
Habits that put health at risk : Some harmful addictive habits like smoking, chewing tobacco, drinking alcohol or taking drugs put our health at risk. These habits affect health adversely.
Effects of tobacco on the digestive system :
- Mouth, pharynx, alimentary canal and other organs of the digestive system cannot function properly.
- Problems like vomiting, nausea, and headache occur due to tobacco.
- Tobacco particles stick to teeth, gums and skin of the mouth cavity and spoil oral hygiene.
- The pharynx and intestine become inflamed and the condition further progresses into cancer leading to death.
Our Role : We should never get addicted to any bad habits. We should also spread awareness about the addiction.
Important days :
- World No Tobacco Day : 31st May
- World Health Day : 7th April
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 11 : Cell Structure & Micro-organism - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-13-Changes - Physical and Chemical- Online Notes |