Map Scale
Maharashtra Board -Class 8-Geography-Chapter-9
Notes
|
Topics to be learn : Surveying and map making Types of Map scale :
The importance of Graphical scale : Maps according to scale :
|
Surveying and map making :
Regional map :
- A particular region is thoroughly surveyed before its map is prepared.
- The distances between various points on a ground are measured during survey.
- To show the distances between various points on a ground on a map, the ratio of the map distance to the ground distance is prepared.
World map :
- In the preparation of world maps, the picture is first surveyed.
- At that time after special observation a scale is fixed.
- Using this scale, an outline map of the whole earth or a part of it is prepared.
- It is possible to view all the countries of the world on one map by using scale in a map.
Remember : Title, subtitle, index, direction arrow, etc. are the other elements of maps. All these elements facilitates map reading.
Map scale :
- The scale of a map is an important consideration.
- Map scale is the ratio of map distance to ground distance.
- Some geometrical and mathematical conversions are performed in order to display the actual ground distances on paper.
- In a map, the map scale must be mentioned. Map scale assists in map reading by providing the actual ground distance between any two spots depicted on a map.
Types of map scale :
Verbal scale : A scale in which distances are expressed with the use of words indicating measurement is called verbal scale.
- For example, 1cm = 100 km.
- In verbal scale, the word indicating measurement on the left hand side indicates the distance between any two points on a map. On the other hand, the word indicating measurement on the right hand side indicates the ground distance between those two points.
- When the map is reduced or enlarged by taking its photo copy, the verbal scale on the original map does not change.
Numerical scale : A scale in which distances are expressed as ratio is called numerical scale.
- For example, 1 : 10000. It is also known as representative fraction.
- In numerical scale, the same measuring unit is used for the figures on the left hand side and right hand side. However, no words are used to indicate this measuring unit.
- In numerical scale, number 1 on the left hand side indicates the distance between any two points on a map. On the other hand, the number 10000 on the right hand side indicates the ground distance between those two points.
- When the map is reduced or enlarged by taking its photo copy, the numerical scale on the original map does not change.
Linear scale : A scale in which distances are expressed by drawing graphical scale is called linear scale.
- For example :
Surveying and map making :
Regional map :
- A particular region is thoroughly surveyed before its map is prepared.
- The distances between various points on a ground are measured during survey.
- To show the distances between various points on a ground on a map, the ratio of the map distance to the ground distance is prepared.
World map :
- In the preparation of world maps, the picture is first surveyed.
- At that time after special observation a scale is fixed.
- Using this scale, an outline map of the whole earth or a part of it is prepared.
- It is possible to view all the countries of the world on one map by using scale in a map.
Remember : Title, subtitle, index, direction arrow, etc. are the other elements of maps. All these elements facilitates map reading.
Map scale :
- The scale of a map is an important consideration.
- Map scale is the ratio of map distance to ground distance.
- Some geometrical and mathematical conversions are performed in order to display the actual ground distances on paper.
- In a map, the map scale must be mentioned. Map scale assists in map reading by providing the actual ground distance between any two spots depicted on a map.
Types of map scale :
Verbal scale : A scale in which distances are expressed with the use of words indicating measurement is called verbal scale.
- For example, 1cm = 100 km.
- In verbal scale, the word indicating measurement on the left hand side indicates the distance between any two points on a map. On the other hand, the word indicating measurement on the right hand side indicates the ground distance between those two points.
- When the map is reduced or enlarged by taking its photo copy, the verbal scale on the original map does not change.
Numerical scale : A scale in which distances are expressed as ratio is called numerical scale.
- For example, 1 : 10000. It is also known as representative fraction.
- In numerical scale, the same measuring unit is used for the figures on the left hand side and right hand side. However, no words are used to indicate this measuring unit.
- In numerical scale, number 1 on the left hand side indicates the distance between any two points on a map. On the other hand, the number 10000 on the right hand side indicates the ground distance between those two points.
- When the map is reduced or enlarged by taking its photo copy, the numerical scale on the original map does not change.
Linear scale : A scale in which distances are expressed by drawing graphical scale is called linear scale.
- For example :
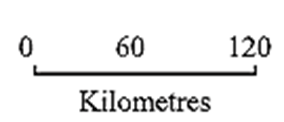
- Compass or blade of grass is used if the ruler is not available for the measurement.
- A thread is used for measuring the curved distances between two points shown in a map.
- When the map is reduced or enlarged by taking 1ts photo copy, the linear scale drawn the original map changes as per the changing size of the map.
The importance of Graphical scale :
- When the map is reduced or enlarged by taking its photo copy, the verbal and the numerical scale on the original map does not change. However, the linear scale drawn on the original map changes as per the changing size of the map.
Large scale maps :
- When a particular part of ground covers comparatively more area on a map, it is called large scale map.
- A map having a numerical scale of 1: 10,000 or less than it is called large scale map.
- Maps of villages, church, agricultural fields, etc. are the large scale maps.
Small scale maps :
- When a particular part of ground covers comparatively less area on a map, it is called small scale map.
- A map having a numerical scale greater than 1 : 10,000 is called small scale map.
- Maps of state, country, continent, world, etc. are the small scale maps. Maps in an atlas are the small scale maps.
Click on link to get required pdf from store :
Class 8-Geography-Chapter-9-Map Scale-Notes
Class 8-Geography-Chapter-9-Map Scale-Solutions
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 8-Industries -online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 10-Field Visit -online Notes |