Composition of Matter
Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter-6
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Two principal Ways of classifying matter are :
- On the basis of physical state.
- On the basis of chemical constitution.
States of matter : On the basis of physical state the various states of matter are solid, liquid and gas.
- Example -Ice is a solid, water is a liquid, and steam is a gas.
- The smallest particles of matter are called atoms.
Types of matter : On the basis of chemical constitution the types of matter are element, compound and mixture.
Characteristics of the states of matter :

Solid : A substance which has a definite shape and volume is called a solid.
- In solid The strength of intermolecular forces are strong enough to keep the particles of solid very close to each other and vibrate at their fixed positions.
- Due to this, solids get properties like definite shape and volume and also high density and non-compressibility.
Liquid : A substance which does not have a definite shape, but has a definite volume is called a liquid.
- In a liquid intermolecular forces are not Strong enough to keep the particles together in fixed positions, as a result liquid has Indefinite shape.
- Though it is not strong enough to fix the particles in definite position, it is strong enough to hold them together. As a result, liquids have definite volume. Liquid have fluidity and their shape is not definite but changes in accordance with the container.
Gas : In a gas intermolecular forces are very weak and the distance between the particles is very large, they move freely and occupy all the available space, as a result gas has indefinite volume and shape.
Fuidity : Liquids flow easily and change their shapes in response to external forces. This property of liquids is called fluidity. It is exhibited by gases also.
Elasticity : Some solids undergo a change in their shapes and volume when subjected to external forces and regain their original shapes and volume on removal of the forces, This property of solids is called elasticity
Plasticity : Some solids are deformed by external forces and do not regain their original shapes on removal of the forces, This property of solids is called plasticity.
Element : A type of matter composed of only one kind of substances where each smallest indivisible part of it has the same properties is Called an element. It cannot be subdivided into simpler substances by any Physical or chemical means.
Characteristics of Element :
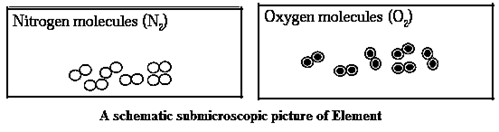
Types of elements :
Compound : A substance produced by a chemical reaction of two or more elements combined in a fixed proportion is called a compound.
Characteristics of Compound :
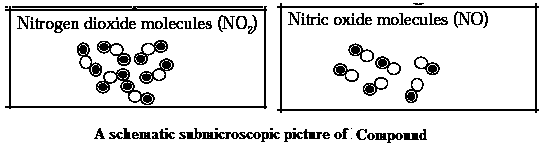
Types of compounds : Organic compound : The compound which when heated strongly gives black coloured carbon residue is called an organic compound, pound or carbon compound Inorganic compound : Compounds which when heated strongly decomposes to give a residue behind are called inorganic compounds. Complex compound : The molecules of compounds which have a complex structure formed by many atoms and in the centre of this structure metal atoms are also included are called complex compounds.
| Water : A compound :Pure Water is a compound formed by chemical combination of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. Whatever may be the source of water, the proportion of its constituent elements oxygen and hydrogen by weight is always 8: 1. Hydrogen is an inflammable’ gas while oxygen gas supports combustion. However, the compound water formed by chemical combination of the gaseous elements hydrogen and oxygen is a liquid. It is neither inflammable nor does it support combustion. On the contrary it helps to extinguish fire. |
Mixture : When two or more elements or compounds which do not react chemically with each other are mixed in any proportion, a mixture is formed.
Characteristics of Mixture :
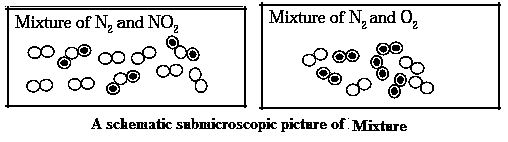
| Milk : A mixture : Milk is a mixture of Water, lactose, fats, proteins and a few more natural substances. The proportion of various ingredients of milk is different as per its source. The proportion of fats in cow milk is 3-5%, while it is 6-9% in buffalow milk. The ingredient water is naturally present in large proportion in milk. Therefore milk exists in liquid state. The sweetness of milk is due to the ingredient called lactose. In other words, the properties of the constituent substances are retained in milk. |
Types of mixtures : Homogenous mixture : When all the components of a mixture form one phase, it is called homogeneous mixture. Heterogenous mixture : . When the components of a mixture are distributed into two or more phases, it is called a heterogeneous mixture.
Q. Why a potassium permanganate solution in water is a homogeneous mixture, while a mixture of oil and water is a heterogeneous mixture ?
(1) In a potassium permanganate solution in water the constituents, i.e. potassium permanganate and water are uniformly mixed throughout. The properties and composition of a homogeneous mixture are the same throughout the mixture. Hence, potassium permanganate solution is a homogeneous mixture. (2) In a mixture of oil and water, the constituents are not uniformly mixed throughout the mixture. The properties and composition of a heterogeneous mixture are not the same throughout the mixture. Hence, a mixture of oil and water is a heterogeneous mixture.
| All the particles of a solid that stay together (or are in the same container) constitute a single phase. (E.g., a heap of stones.)
A liquid substance along with all the soluble substances dissolved in it together constitute a single phase. (E.g. sea water) A liquid or all its drops present together or in the same container constitute a single phase. (E.g., rain drops) The liquids present together or the same container, but not mixed with each other, constitute separate phase, (E.g., oil and water) All the gases present together constitute a single phase. (E.g. air) |
Solution: A homogenous mixture of two or more substances is called solution.
- Solvent : The component of a solution which is present in the largest proportion is called solvent. Examples : (1) In sea water, water is the solvent. (2) In tincture iodine, alcohol is the solvent.
- Solute : The other component of a solution which is present in less proportion than the solvent is called solute. Examples : (1) In sea water, salt is a solute. (2) When a small of amount of sugar is dissolved in water, sugar is the solute in the solution.
Characteristics of a solution :
Types of solutions :
- Liquid in liquid : Example : Vinegar
- Gas in gas : Example : Air
- Solid in solid : Examples : Brass, steel
- Gas in liquid : Example :Chlorinated water.
Suspension : The heterogenous mixture of a liquid and a solid is called a suspension. The diameter of the solid particles in a suspension is larger than 10-4 m. E.g., sand in water.
Characteristics of a suspension.
Colloid : A heterogeneous mixture in which the particles cannot be seen with a naked eye is called a colloid. In which the diameter of particles is around 10-5m E.g. milk, blood.
- The pores of an ordinary filter paper are larger than colloid, the heterogeneous mixture, therefore it cannot be separated by filtration.
Characteristics of a colloid :
Molecular formula : Molecular formula indicates the number of atom of each of the constituent elements present in one molecule of a compound. A molecular formula includes the information regarding the symbols of the all the constituent elements and their respective number as subscripts.
Example :
- Name of the compound – Water
- Molecular formula – H2O
- Constituent elements – H, O
- Number of atoms of constituent elements : H=2, O=1
Valency : The capacity of an element to combine with another element is known as valency.
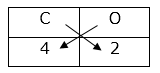
Cross multiplication method for writing the molecular formula of simple compounds Step 1 : Write the symbols of constituent elements.
Step 2 : Write the valency below the respective element.
Step 3 : Cross multiply the valencies. Step 4 : Write the formula of the compound obtained by cross multiplication. C2O4 Step 5 : The number of constituent atoms in the final molecular formula should be the smallest possible whole numbers. For getting this, divide the formula obtained in step 4 by a suitable number. Formula obtained by cross multiplication : C2O4 Final molecular formula obtained by dividing by 2 : CO2
C
O
C
O
4
2
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : MSBSHSE -Class 8th Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Videos : Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science Videos - watch chapter wise topic wise videos of all chapters Previous Chapter : Chapter 5: Inside The Atom - view online notes Next Chapter : Chapter 7- Metals and Nonmetals -view online notes |
Good