Metals and Non-Metals
Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter-7
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Elements : Elements are classified into three general types, metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Examples :
- Metals : Aluminium, copper, iron, steel, stainless steel.
- Non-metals: chlorine, iodine, oxygen.
- Metalloids : Silicon, Germanium.
Physical properties of metals :
- Metals have a lustre.
- The metals are hard.
- Metals are malleable. They can be beaten into thin sheets.
- Metals are ductile. They can be drawn into wires.
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- At ordinary temperature, metals are generally solid. (Exception : Mercury is liquid.)
- Metals usually have high density.
- Metals have high melting points and boiling points.
- Metals are sonorous.
Physical properties of non-metals :
- Non-metals do not have lustre.
- Non-metals are not malleable and ductile.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- At normal temperature, non-metals are in the solid, gaseous and liquid states.
- Non-metals have low density.
- Solid non-metals are brittle.
- Non-metals have low melting and boiling points.
Metalloids : Metalloids have properties which are intermediate between metals and non-metals.
Chemical properties of metals:
Electronic configuration : Electronic configuration is the basis of chemical behaviour of elements.
Majority of metals have upto three electrons in their outermost shell.
Examples :
- 11Na à Atomic number :11, Electronic configuration : 2, 3, 1
- 12Mg à Atomic number :12, Electronic configuration : 2, 8, 2
- 13Al à Atomic number :13, Electronic configuration : 2. 8. 3
Formation of ions : Metals have a tendency to lose their valence electrons to form positively charged ions, i.e. cations.
Na → Na+ + e- : (Sodium → Sodium ion)
(2,8,1) (2,8)
Mg → Mg++ + 2e- : (Magnesium → Magnesium ion)
(2,8,2) (2,8)
Al → Al+++ + 3e- (Aluminium → Aluminium ion )
(2,8,3) (2,8)
Reaction with oxygen : Metals combine with oxygen to form their oxides.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal oxide
The metal oxides are basic in nature.
Metal oxides react with an acid to form salt and water.
Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
Reaction with acid : Most of the metals react with dilute acids to form metal salts and hydrogen gas.
Metal + dilute Acid → Metal salt + Hydrogen gas.
Reaction with water : Most metals do not show any observable and fast reaction with cold water. But some metals like sodium and potassium react vigorously with cold water to produce their hydroxides and hydrogen gas. Magnesium metal requires steam or hot water to give their oxide and hydrogen.
Q. How will you show that metal oxides are basic in nature?
- Take magnesium oxide in a test tube. Add water in the test-tube. Shake the test-tube. Test the solution with red and blue litmus paper. Blue litmus paper remains as it is while red litmus paper turns blue. This shows that metal oxides are basic in nature.
- Metal oxides react with an acid to form salt and water. Therefore, metal oxides are basic in nature.
Chemical properties of non-metals :
Electronic configuration : Most of the non-metals have 4 to 7 electrons in their valence shells.
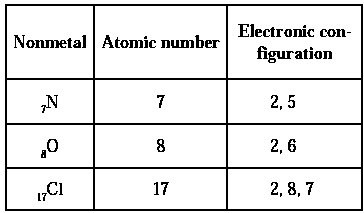
Formation of ions : Non-metals have a tendency to accept electrons in their valence shell to form negatively charged ions called anions.
Cl + e- → Cl- (Chlorine àChloride ion)
(2,8,7) (2,8,8)
O + 2e- → O--( Oxygen à Oxide ion)
(2,6) (2,8)
N + 3e- → N--- (Nitrogen Nitride ion)
(2,5) (2,8)
Reaction with oxygen : Non-metals combine with oxygen to form their oxides.
Non-metal + Oxygen à Non-metal oxide
The oxides of nonmetals are acidic in nature. They react with bases to form soluble salt and water.
C + O2 → CO2
CO2 + 2NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
The oxides of nonmetals react with water to form an acid.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 Carbonic acid
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3 Sulphurous acid
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 Sulphuric acid
Nonmetals do not react with dilute acids.
Noble metals : Some metals like gold, silver, platinum, palladium and rhodium are found in nature in the form of elements. They are not affected by air, water, acids and heat etc. Hence, they are called noble metals.
Use of Noble metals :
- Gold, silver and platinum are used to prepare ornaments.
- Silver is used in medicines. (it has antibacterial property).
- Gold and silver are also used to make medals and few electronic devices.
- Platinum, palladium metals are used as catalyst.
Purity of gold : The purity of gold is measured in carats. 24-carat is considered as gold of 100% purity. 24-carat gold is pure and very soft. 100% pure gold bends or breaks easily. Therefore, copper or silver is added to gold in the necessary proportion while making ornaments.
|
Corrosion : Gases in the air react with metals in presence of moisture to form metal compounds on the surface. The metals get affected by this process and undergo corrosion.
Alloys :
- A homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or of metals and non-metals is called an alloy.
- They contain metals in specific proportions.
- The physical properties of an alloy are different from those of its constituents, but chemical properties remain the same.
- Copper and tin are used to make an alloy called bronze. It is hard and corrosion resistant.
- When iron and carbon are mixed, an alloy steel is formed. It is a stronger material.
- The alloy, stainless steel is made from iron, carbon, nickel and chromium. It is more durable, clean and does not rust.
| 1-There is an iron pillar in the premises of Kutubminar in Delhi. made about 1500 years ago. The pillar is lustrous even after so many years. This is because our ancestors had made it from an alloy. It contains small proportion of carbon silicon and phosphorous in Iron.
2-A cheap variety of stainless steel is made sometimes by using copper instead of costly nickel. You might have seen the vertical cracks in stainless steel vessels. The reason is as above. |
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 6: Composition of Matter - view online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 8- Pollution - online Notes |