Pollution
Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter-8
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Pollution : Contamination of natural environment, causing harmful to ecosystems is called as pollution.
Industrialization, increasing population, mining, transportation, indiscriminate use of pesticides and fertilizers, etc. are all man-made causes that is degrading the environment of the earth. Due to all these activities pollution of various kinds is created. This affects all the living organisms including human beings.

- The first picture shows, there are factories on the bank of water. From the factories toxic effluents are released into the water body without any treatment. This is a water pollution.
- In the second picture, a car is seen emitting smoke. This is creating air pollution.
- The third picture too shows exhaust gases being released by the huge thermal power plants, into the atmosphere. This is creating air pollution.
- Similarly, the factories are also letting out toxic gases in the air. This also creating air pollution.
From all these pictures, a common fact seen is that responsibility of environment protection is not undertaken by anyone. Due to insensitive attitude of human beings, every ecosystem is heavily polluted.
Control of all types of pollution is an important aspect. Man is only thinking of economic development. Due to this, pollution is reaching hazardous levels.
Pollution around us: Pollution is seen in entire surroundings.
- The water bodies are heavily polluted due to released effluents.
- Oceans, rivers, tanks, ponds, canals are considered as the place where one can release indiscriminately all the pollutants.
- Various types of pollutants are released through the industrial effluents and domestic sewage which are mixed in the water.
- In fields, on land or soil everywhere solid waste pollutants are dumped anyhow. Farms experience heavy pollution due to insecticidal sprays and chemical fertilizers.
- In air, various toxic gases and particulates are released due to industries and vehicular traffic.
Causes of pollution :
- Some pollution occurs due to natural causes, such as forest fires, dust storms, volcanic eruptions, etc. But pollution to a greater extent and on regular basis is due to activities of human beings.
- Man-made pollution is caused in every possible ecosystem.
- When we try to produce industrial products of our own choice, many hazardous substances are inadvertently added as pollutants to the environment.
- This causes pollution of air, water and land too.
Pollutants : Pollutants are the factors that adversely impact natural functions of ecosystem causing harmful effects on abiotic and biotic components of the ecosystem.
They are hazardous and cause toxic and hazardous effects depending upon all the living organisms.
Two types of pollutant : (1) Natural (2) Man-made
The natural pollutants are degraded naturally after certain duration of time. But man-made pollutants persist for a long period of time.
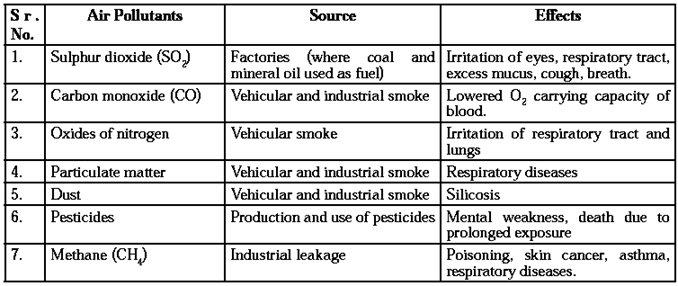
Air pollution : Air pollution is the contamination of air by harmful substances like poisonous gases, smoke, particular to matter, microbes, etc.
Reasons of air pollution :
(A) Natural reasons :
- Volcanic eruption : Pollutants- Solid, gaseous and liquid materials like Hydrogen sulphide. sulphur dioxide, carbon dioxide, ammonium chloride, hydrogen, vapours, dust
- Earthquake: Pollutants- Poisonous gases and water vapours present in the interior of the earth
- Cyclones arid dust storms : Pollutants- Dust, soil, garbage, pollens, microbes
- Forest fires : Pollutants- Carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, hydrogen sulphide, smoke.
- Microbes in air : Pollutants- Pollens of Parthenium, spores of bacteria, fungi.
(B) Man-made reasons :
- Burning of fuel (coal, timber, LPG, kerosene, diesel, petrol):Burning of solid waste, agricultural waste, etc : Pollutants- carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, sulphur dioxide, lead compounds
- Industrialization : Pollutants -Burning of solid waste, agricultural waste, etc.
- Atomic energy plants and atomic blasts : Pollutants-Burning of solid waste, agricultural waste, etc.
Peeping in the history : Some notorious episodes of air pollution :
- In London, during 5th to 9th December 1952 and 3rd to 7th December 1962 there was thick smog due to smoke emitted by combustion of coal which mixed with fog forming smog.
- In 1948 in the city of Petersburg, smoke and soot spread so much that the entire city appeared dark as night during a day time. This city was then called black city.
- Union carbide company in Bhopal suffered from an accident when the toxic methyl isocyanate gas was leaked killing 8000 people and making few more thousands disabled forever. This incidence happened on the night of 2nd December 1984. This incidence is known as Bhopal Gas tragedy. It is said to be the worst ever industrial accident.
Effect of air pollution on plants and animals :
Effects on plants :
- Stomata are choked due to dust particles,
- Rate of photosynthesis declines.
- Plant growth is retarded.
- Yellowing of the leaves resulting into their fall
Effects on animals :
- Animals cannot respire properly
- Irritation to eyes and throat.
Ozone layer : Below the stratosphere ozone layer is present. The infra-red and ultraviolet rays (UV-B) in the solar radiations do not reach the earth’s surface due to the ozone layer. This layer works as an umbrella helping in protection of living organisms, including plants and animals. If ozone layer is not present, the flora and fauna on the earth will have to face hazardous effects such as cancer.
Reasons for depletion in ozone layer :
Chlorofluorocarbons are air pollutants which are responsible for the destruction of ozone molecules. One molecule of ozone reacts with many molecules of ozone causing the destruction of ozone molecules. These substances were used as coolants in refrigerator, aerosol sprays and in jet propellants. Due to use of these substances, there is depletion in ozone layer.
Effects of air pollution on atmosphere :
Depletion in Ozone layer : Below the stratosphere ozone layer is present.
Ozone layer is a protective layer that helps the living world of the earth from ultraviolet rays (UV-B) present in the solar radiation. One of the effects of air pollution is destruction of ozone layer.
Greenhouse effect and Global warming : CO2 is present in very small quantity in the atmosphere around Earth. It absorbs radiated heat from the solar radiation. Due to CO2 there is warmth on the earth’s surface. However, in recent times there has been continuous increase in the amount of CO2 due to continuous growth of industrialization and burning of fossil fuels. This CO2 is forming an additional covering around the earth along with other gases such as Nitrous oxide, methane and CFC. This layer does not allow the re-radiation of the solar heat but traps the same. This causes warming of the Earth. All of these gases are called greenhouse gases. They bring about greenhouse effect. Greenhouse effect is causing global warming.
Greenhouse effect on environment :
- Global warming
- Climate Change
- Decrease in the agricultural yield,
- Threat to wildlife
- Melting of glaciers and icebergs resulting into sea-level rise and coastal land submergence,
Acid Rain :
- When timber, coal and fossil fuels are burnt they release oxides of sulphur and nitrogen into atmosphere.
- These get dissolved in rainwater and turn into acids like sulphuric acid, nitric acid, nitrous acid, etc.
- When there is rainfall, the acids fall on the ground in the form of acid rain.
- Sulphur containing air pollutants affect the colours in paints, oil paintings and materials such as nylon, cotton fabrics, leather articles and papers, etc.
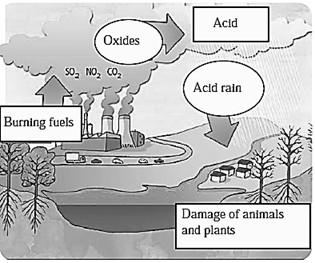
Effects of acid rain :
- Soil and water bodies become acidic.
- This causes harm to resident animals and plants. The entire ecosystem is threatened.
- Due to acid rain, erosion of buildings, bridges, metal idols, busts, historical monuments, wire fences, etc. get rusted.
- Plants absorb the heavy metals. Heavy metals such as cadmium and mercury indirectly enter the food chain through plants.
- Water is acidified. It enters the pipes causing leaching of metal and plastic material. This results in serious health problems.
Air pollutants: Sources and effects
Preventive measures of air pollution:
- The exhaust gases from the factories should not be left into the atmosphere without proper treatment. The polluting particulates should be filtered through proper machinery. The arresters and filters should be used for this purpose.
- Proper management should be done to dispose solid waste material which stinks.
- The atomic testing, chemical weapons, etc. should be totally banned for the betterment of the earth.
- CFC should be either controlled or banned to protect the ozone layer.
Air Quality Index : The air quality index, proportion of SO2, CO, NO2, ozone, particulate matter, etc. is measured every day in big cities. This information
is displayed on the boards for the citizen for their knowledge. The extent of air pollution in the city is thus known by air quality index.
Water pollution :
Water is called as molecule of life : Surviving without water is impossible. No animal or plant can sustain life without water. Therefore water is called as molecule of life. The animal and plant bodies are also made up of water to some extent. All the bodily reactions are possible only due to water.
Uses of water : We need water for drinking and cooking. It is also necessary for cleaning, for irrigation of the fields and farms. Water is needed in industries for various processes. We also use water as a medium for transport.
Sources of water : 71% of the earth’s surface is occupied by water.
We can use the water from unpolluted sources which are not acidic.
Water from rivers, ponds, lakes, stream, canals, etc. can be used if it is pure and safe.
Water pollution: When the water becomes unclean and toxic due to mixing of natural or artificial polluting substances, then it is called water pollution.
- Pollutants cause water to become toxic and unclean.
- The dissolved oxygen content in water becomes less causing harm to the resident living organisms.
- Disease causing epidemics break due to pathogens added to the water due to pollution.
- Physical, chemical, and biological changes in the water are caused due to water pollutants.
Reasons of water pollution :
- In big cities, the domestic sewage and industrial effluents are released in the water. This causes pollution of the water bodies.
- In rural areas, the river waters are used for washing, bathing, swimming, washing the cattle, etc.
- Many people also use river banks for defecation and urination. All such activities cause pollution of the water.
Type of water pollutants :
- Biological : Algae, bacteria, viruses, parasites
- Inorganic : Suspended particles like fine sand, dust, soil, precipitates of salt, compounds of arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury, and traces of radioactive material
- Organic : Weedicides, insecticides, fertilizers, sewage, industrial effluents, etc.
Natural causes of the water pollution :
- If organic pollutants are added to the water there is overgrowth of weeds such as Eichhornia. The growth ol‘ algae also makes the water unsuitable for consumption. These aquatic plants release oxygen during day time but by night they require oxygen thus depleting the dissolved oxygen level. The natural characters of water are then changed.
- The decomposing matter when added to the water make it polluted and stinking.
- Due to deposition of sludge or eroded soil, the rivers change their path and divert from original flow. The currents are also changed. Deposition of sludge makes the water polluted.
- Due to soil erosion, surrounding the water bodies, the microbes, bacteria, protozoans and the worms and larvae of nematodes enter the water causing severe biological pollution. Many inorganic pollutants are also added to the water. The fungi and bacteria present in the water make it non-potable. Such water spreads the water-borne diseases.
Man-made reasons for water pollution :
The effluents and other substances released by man into the surrounding water bodies together can be pulled man-made reasons for water pollution.
- Domestic sewage : The excreta, urine and other domestic-use water is added to the water bodies in many cities and villages. In big metro-cities, the sewage is partially treated but these management practices are not enough.
- Industrial effluent : Different industries and factories release effluents which may contain toxic and harmful components, such as various pigments, bleaching chemicals, leather pieces, fibres, mercury, lead, etc.
- Oil pollution : Oil spillages are seen in the seas due to leakage of crude oil. The crude oil is hazardous as it contains cancer causing hydrocarbons.
- Fertilizers and pesticides : These compounds when used in farm, may get washed off to nearby water body. The chemical fertilizer containing N, P, K cause water pollution. Pesticides such as endrin, chlorine, carbonate containing pesticides, etc. are mixed with water. They cause contamination of the aquatic animals.
- The wrong behaviour of human beings causes water pollution. The addition of wastes, defecation near coasts, washing clothes, decomposing hemp and flax in water, disposal of ashes, floral offerings to god, dumping ashes all such activities result into water pollution.
- The warm water released into the water body through thermal power plants cause thermal pollution.
Effects of water pollution on human beings :
Effects of water pollution on the ecosystem : Biological effects : Abiotic effects :
Soil pollution : Physical, biological and chemical properties and the fertility of soil is decreased due to either natural or man-made cause. Such a condition that results into lesser productivity of the soil is called soil pollution.
Effects of soil pollution :
Relationship of soil pollution with air and water pollution :
Types of waste and examples : 2) Plastic 3) Glass pieces 4) Old utensils, clothes 5) Tins and cartons of used items, the discarded household items. 2) Urine and faeces 3) Peels of fruits, stalks of vegetables and fruits. 4) Food waste 5) Garlands and old bouquets. 2) Cattle dung and urine 3) Some persistent amount of insecticides 4) Some amount of fertilizers 5) Empty containers, bags, cartons of insecticide, chemical fertilizers, seeds, gunny bags, etc.
Domestic waste :
Biological waste
Agricultural waste :
1) Empty containers of medicines, papers, bottles, etc.
1) Dead corpse of animals.
1) The stubs of crops after the grains are removed.
Pollution- Prevention and control : Government of India has enacted some laws for control, regulation and prevention of pollution.
These laws are followed in order to keep the environment pollution free.
Government statutory bodies : Various laws and rules are in force in relation to biomedical waste, harmful effluents, solid waste and sound pollution.
Government statutory bodies like Maharashtra Pollution Control Board and Central Pollution Control Board supervise about whether the industries, industrial areas, local governing bodies like municipalities, district councils, panchayat samiti, gram panchayat, etc. follow the laws about pollution control.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 7: Metals and Non-metals - view online Note Next Chapter : Chapter 8- Disaster Management -view online Note |