|
Topics to be learn :
- Earthquake
- Fire
- Landslide/Rift collapse
- Disaster-relief planning
|
Disaster : Disaster is the sudden event that causes large scale damage to life, property and social aspects of a nation and society.
Types of disasters : The main types of disasters are natural and man-made disasters.
Earthquake : Sudden vibrations on the earth and shaking of the earth surface /ground is called an earthquake.
- The earthquake is caused due to seismic waves. These waves cause movements of the earth’s surface which are perceived as tremors or shaking.
- The vibrations cause the surface of the earth to go up-down. The resulting shocks and waves formed in the interior of the earth spread on the surface in all directions.
General Effects of earthquake :
- The buildings and houses collapse causing severe damage to life and property.
- The water and electricity supply is disrupted causing inconvenience to people.
- People get trapped in rubble and may lose their lives.
The central point of earthquake : The point above the epicentre on the earth’s surface is called central point of the earthquake. In this area there is a major loss as the strong waves reach the epicentre first.
Shocks of earthquake & measurement :
Shocks of earthquake :
- Mild : Shocks are in more frequency, but destruction is less.
- Acute or Intensified : Frequency of shocks is much less but major destruction is caused.
12,400 to 14,000 earthquakes occur on the earth per year. Daily there is occurrence of earthquake somewhere on the earth.
National Earthquakes information centre has carried out all such observations.
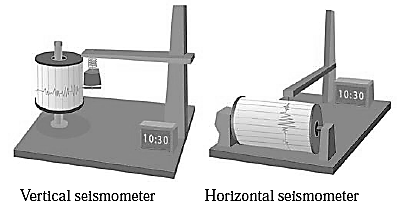
Seismograph or Seismometer : Instrument which records the earthquakes.
Richter Scale : The mathematical measure to understand the accentuation (intensity) of earthquake.
[collapse]
Causes & Impact of an earthquake :
Causes of an earthquake :
- Natural causes : (1) Volcanic eruption (2) Steam formed in the interior of Earth tries to come out on the earth’s surface.
- Causes due to actions of human beings : (1) Underground atomic tests. (2) Mining. (3) Pressure due to mega-hydroelectric projects and dams.
Impact of earthquake :
- Biological impacts : Wild animals and domestic animals are killed. Loss of life for human beings. Destruction of biodiversity. Ecosystems endangered.
- Economic Impacts : Economic loss, destruction of infrastructure. Electric poles, pipelines, houses, buildings, roads, railway tracks, etc. are completely destroyed. Urban regions may face dangers of fire.
- Geographical Impact : Flow of rivers and streams are changed. Tsunami waves are formed. The coastal region are largely affected due to devastating tsunamis. Level of groundwater table either decreases or increases.
[collapse]
Spoiler
Precautions to be taken at the time of Earthquake (Dos):
If you are at home :
- Not to get scared, not to run helter-skelter.
- Stand silently at one place.
- Or sit on the ground under a table or other furniture.
- Wait there till the movement of the earth stops.
- Protect your head and face by covering it with folded hands.
If outside the home :
- If travelling in the vehicle, park your vehicle at a safe place and be inside the vehicle.
- Avoid waiting below tall buildings, trees or electric pole.
Avoid doing following things during earthquake (Don’ts)
- Not to use elevator at the time of earthquake.
- Do not sit in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
- Do not be motionless for a long time.
- Short circuit may break into fire therefore do not keep the main electric connections switched on. Turn off the mains.
- Not to use candles, lantern or matchbox. It may break into fire. Instead use torches.
[collapse]
Earthquake Resistant Buildings : The Earthquake Resistant buildings are constructed with the idea that even if there is some movement of the earth, the building should not get damaged.
Code of conduct :
‘Indian Standard Institute’ has made some code of conduct.
- Buildings are constructed as per I.S. 456
- Earthquake resistant constructions (Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structure) are performed as per IS 1893
- Ductile detailing of reinforced concrete structures subjected to seismic forces as per IS 13920
- Advanced technology is used for earthquake resistant construction.
[collapse]
Modern equipment that give prior intimation about earthquake : Laser ranging, very long base line, Geiger counter, creep meter, strain meter, tide gauge, tilt meter, volumetric strain gauge, etc.
Fire : Fire can be due to natural reasons as it is in the case of natural forest-fires. It can also be due to man-made reasons when the fire may be intentional or unintentional.
Types of fire :
Types of fire : There are five types of fire. This division is based on two criteria, viz. (i) Which substance is being burnt. (ii) What is the method of extinguishing it.
- Class A Fire : Commonly flammable materials like wood, clothes, coal, papers etc. are their fuel source. This fire is extinguished by spraying water over it. This is also called cooling out. Water is effectively used to put off class A fire.
- Class B Fire: Flammable liquid Substances such as petrol, oil, varnish solvents, cooking oil, paints, etc. catch fire and it is called class B fire. Since these substances are lighter than water, they can be extinguished only by foaming fire extinguishers.
- Class C Fire : The fire caused due to gaseous substances is called class C fire. Domestic gas (L.P.G.) and acetylene can cause such kind of fire.
- Class D Fire : Combustible metals catch class D fire. Metals such as potassium, sodium and calcium, can react with water at normal room temperature whereas magnesium, aluminium and zinc react with water at high temperature. When both these groups combine with water, it causes explosion.
- Class E Fire : When electric components are subjected to fire, they form class E fire. Such fires can be caused by short circuit or due to problems in electric fittings. Such fire is extinguished with the help of carbon dioxide and non-conductive fire extinguishers.
[collapse]
Methods of Fire Extinguishing :
Methods of Fire Extinguishing : Two important aspects of fire control are : (1) To stop the fire (2) To prevent it from spreading further.
There are three main methods to extinguish the fire. These methods are used to stop the spread of fire and to avoid the financial and other losses.
- Cooling out by use of water : Water is easily available and can be used for putting off fire instantly. Due to spraying of water, there is cooling effect produced which helps in reducing the loss by fire. Fire can be easily controlled by water.
- Suppressing the fire by covering it : When there is a fire due to electricity or oil it has to be controlled by covering the fire by sand or soil. When the froth is spread on the fire, there is no contact between air and fire. This puts off the fire and stops the spread of fire caused due to oil.
- Keep away Flammable Substances ; Care is taken to keep away all flammable substances from the fire. Wooden articles and inflammable substances are kept in such as way the fire will not engulf it. Stirrup pumps are used to put off small fires by which the water is spread in all directions around the fire.
[collapse]
Precautions and safety measures to stop the fire :
Precautions and safety measures to stop the fire :
- Switching off the regulator of cooking gas cylinder when not in use. Put off the connections of all electrical appliances when not in use.
- If there is fire, call others immediately for help. Take help of others by calling them. Also help others who are in need to save their lives from fire.
- Get help from fire brigade by calling phone number 101.
- Know details about working of the fire extinguishing apparatus.
- Give first aid to the victim of fire. Seek immediate medical help.
[collapse]
Landslide/Rift Collapse : There are natural cracks and fissures in hard rocks which result into their breaking at the time of heavy rains. The cracks widen due to flowing water which further causes weathering process. The heavy rocks slide on the sloppy region and collapse to the lower side. A collapse of a mass of earth or rock from a mountain or cliff due to some sudden cause is called a landslide.
Causes & Effects of landslide :
Causes of landslide :
- Major natural disasters such as earthquake, tsunami, heavy rains, storms, floods cause landslide.
- Unlimited cutting of trees causes soil erosion leading to land slide.
- While building roads in mountains, there is a lot of digging, that makes the mountain weak resulting into landslide.
Effects of landslide :
- Rivers get flooded.
- Rivers change their path.
- Waterfalls are displaced, and they change their original position.
- Artificial reservoirs are formed.
- The trees are uprooted and the plant life in general is destroyed.
- The constructions done on the slope collapse.
- There is large scale loss of life and property as the villages are buried under the debris.
- The debris and rocks on the rail tracks or roads cause suspended traffic.
[collapse]
Disaster relief - planning : Disaster relief plan is specially done to monitor and manage the conditions when disaster strikes. The urgent relief work is necessary during any disasters and hence this kind of preparations are necessary.
- Anyone can face disaster at any time. The only way to tackle with such disasters is to keep preparedness to deal with any calamity.
- Schools, colleges and various offices need to chalk out a detailed planning in case of possible disasters.
Disaster relief planning for school :
Disaster relief planning for school:
Display Primary information of the school :
- Name and address of the school
- Name and residential address of the Head Master with contact number.
- Names and contact numbers of school management members.
- Total number of staff.
Structure of School Disaster Management Committee :
- Fire extinguisher
- Awareness
- Instructions
- Traffic Management
- Safety f. communication committee (2-3 members/ sub-committee)
Detailed information about school building :
- Total number of rooms.
- Number of classroom.
- Classes.
- Type of roof (wooden/cement/sheets)
- Age of the building, building year.
Information about school ground :
- Type of the playground, prayers space, types of play grounds etc.
- Distance of the ground from main road.
Daily routine of the school :
- At what time the school starts and what time does it end.
- Daily activities taking place in the school.
Possible hazards in the school :
- Name and type ( normal/ medium/ acute) of the danger.
- Destruction in the past and current planning.
Disaster management map of the school to be included :
- All buildings of the school, their structure, grounds, entrances, place of probable dangers in the school, safe places at the time of disaster, nearest road.
- This map must be at the entrance of the school and all students must be given detailed knowledge about it.
[collapse]
Institutes & work of the institutes in disaster relief management :
Institutes & work of the institutes in disaster relief management :
| Institutes |
Function |
| Indian Mountaineering Institute, Institute of geology, World geological forum |
Program to forecast the land slide and its effects. |
| National Institute of Seismology. |
Research work related to earthquakes and allied disaster relief work. |
[collapse]
