Measurement and Effect of Heat
Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter-14
Solution
Question 1:
A. Whom should I pair with?
| Group A | Group B |
| a. Temperature of a healthy human body | i. 296 K |
| b. Boiling point of water | ii. 98.6 0F |
| c. Room temperature | iii. 0 0C |
| d. Freezing point of water | iv. 212 0F |
Group A
Group B
a. Temperature of a healthy human body
ii. 98.6 0F
b. Boiling point of water
iv. 212 0F
c. Room temperature
i. 296 K
d. Freezing point of water
iii. 0 0C
B. Who is telling the truth?
a. The temperature of a substance is measured in Joules.
False. - The temperature of a substance is measured in °C or °F or K.
b. Heat flows from an object at higher temperature to an object at lower temperature.
True
c. Joule is the unit of heat.
True
d. Objects contract on heating.
False. – Generally objects expand on heating. There are some exceptions to this.
e. Atoms of a solid are free.
False - Atoms of a solid are bound to each other due to the forces acting between them.
f. The average kinetic energy of atoms in a hot object is less than the average kinetic energy of atoms in a cold object.
False -The average kinetic energy of atoms in a hot object is greater than the average kinetic energy of atoms in a cold object.
C. You will find if you search.
a. A thermometer is used to measure..........
b. The apparatus used to measure heat is called a .............
c Temperature is the measure of the ........... kinetic energy of the atoms in a substance.
d. The heat contained in a substance is the measure of the .............. kinetic energy of atoms in the substance.
a. A thermometer is used to measure temperature. b. The apparatus used to measure heat is called a calorimeter. c. Temperature is the measures of the averagekinetic energy of the atoms in a substance. d. The heat contained in a substance is the measures of the totalkinetic energy of atoms in the substance.
Question 2.
Nishigandha kept a vessel containing all the ingredients for making tea in a solar cooker. Shivani kept a similar vessel on a stove. Whose tea will be ready first and why?
Shivani's tea will be prepared first, because in a given time, the amount of heat received by the vessel on a stove is far greater than that received by the vessel kept in a solar cooker. Thus, the time taken by the tea to reach its boiling point will be less than Nishigandha’s vessel. Hence, Shivani's tea will be ready first than Nishigandha’s tea.
Question 3.
Write brief answers.
a. Describe a clinical thermometer. How does it differ from the thermometer used in laboratory?
Figure shows a clinical thermometer. As the body temperature of a healthy person is 37 0C, clinical thermometers are designed to measure temperatures between 35 0C and 42 0C. (or from 95°F to 108°F) The thermometer used in a laboratory has wider range and does not have constriction like a clinical thermometer.

b. What is the difference between heat and temperature? What are their units?
determines the direction of flow of heat.
Heat
Temperature
It is a form of energy which causes in us the sensation of hotness or coldness.
It is measure of the degree of hotness or coldness of an object.
Heat is related to the total kinetic energy of the atoms in a substance
Temperature is related to the average kinetic energy of the atoms in the substance.
Heat flows from a body at higher temperature to a body at lower temperature.
Temperature is a quantity that
It is measured in joules (J).
It is measure in kelvin (K), Celsius (oC) and Fahrenheit (oF)
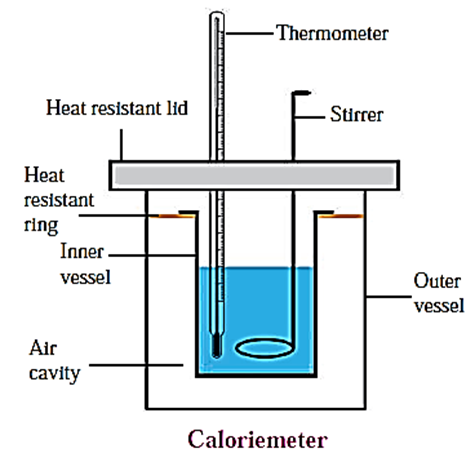
c. Explain the construction of a calorimeter. Draw the necessary figure.
Calorimeter : A calorimeter is used to measure the heat content of an object. Using this equipment, we can measure the heat produced or absorbed in a physical or chemical process. A calorimeter is shown in figure
d. Explain why rails have gaps at specific distances.
All solids expand on heating. As rails are made up of steel, these also expand in summers and contract in winters. Also, they expand due to rise in temperature caused by the friction between the rails and the wheels of the running train. These expansion and contraction can cause sagging and bending of rails which could derail the trains running on them. Thus, the rails have been provided with gaps at specific distance so as to prevent this bending of rails. These spaces get closer in summers and wider in winters.
e. Explain with the help of formulae the expansion coefficients of liquid and gas.
Expansion coefficients of liquid : When a liquid which is held in a container is heated, both the container and the liquid expand. The expansion of the container is usually very small compared to that of the liquid in it. Often, it can be ignored. Suppose, a liquid is heated so that its temperature rises by ΔT (very small) and its volume increases from V1 to V2. Experimentally, it is found that the increase in volume, V2 — V1, is proportional to V1 and DT. Hence, V2 — V1 ∝ V1 ΔT. ∴ V2 — V1 = β V1 ΔT, Where, b is a constant of proportionality called the volumetric expansion coefficient of the liquid. β = \(\frac{V_2-V_1}{V_1ΔT}\) It is expressed in per °C. We have V2 = V1 + βV1ΔT = V1(1 + βΔT) β is the increase in the volume of a liquid per unit original volume per unit rise in its temperature. Expansion coefficients of gas : A gas is enclosed in a container. When it is heated at constant pressure, both the container and the gas expand. Suppose a gas is heated at constant Pressure so that its temperature rises by ΔT (Very Small) and its volume increases from DT (very small) and its volume increases from V1 to V2. Experimentally, it is found that the increase in volume, V2 — V1, is proportional to V1 and ΔT. Hence, V2 — V1 ∝ V1 ΔT ∴ V2 — V1 = β V1 ΔT Where, b is a constant of proportionality, the volumetric expansion coefficient, called the constant pressure expansion coefficient. β = \(\frac{V_2-V_1}{V_1ΔT}\) It is expressed in per °C. We have V2 = V1 + βV1ΔT = V1(1 + βΔT) β is the increase in the volume of a gas per unit original volume per unit rise in its temperature when the pressure is kept constant.
Question 4.
Solve the following examples.
a. What must be the temperature in Fahrenheit so that it will be twice its value in Celsius?
Given : F = 2C, ∴ C = F/2, F= ? We know \(\frac{F-32}{9}=\frac{C}{5}\) ∴ \(\frac{F-32}{9}=\frac{F/2}{5}\) ∴ F−32 = \frac{9F}{2×5}\) ∴ F – 0.9F = 32, ∴ 0.1 F =32 ∴ F = 32/0.1 = 320 0F
b. A bridge is made from 20 m long iron rods. At temperature 18 0C, the distance between two rods is 0.4 cm. Up to what temperature will the bridge be in good shape?
l1 = 20 m, l2 – l1 = 0.4 cm = 4 x 10-3 m, Ti = 18 °C, λ for iron = 11.5 x 10-6/°C l2 – l1 = λl1ΔT ∴ ΔT = \(\frac{l_2-l_1}{ λl_1}=\frac{4×10^{-3}}{11.5×10^{-6}×20}=\frac{400}{23}\) = 17.39 °C Now ΔT = Tf – Ti , ∴ Tf = ΔT + Ti = 17.39 + 18 = 35.39 °C The bridge will be in good shape upto 35.39 °C
c. At 15 0C the height of Eifel tower is 324 m. If it is made of iron, what will be the increase in length in cm, at 30 0C?
Given : ΔT= 30 °C – 15 °C = 15 °C, l1 = 324 m, λ for iron = 11.5 x 10–6/°C l2 – l1 = λl1ΔT ∴ l2 – l1 = 11.5 x 10–6 x 324 x 15 = 55890 x 10–6 m = 55890 x 10–4 cm = 5.589 cm (nearly 5.6-cm) This is the increase in the length, i.e., the increase in the height of Eiffel Tower.
d. Two substances A and B have specific heats c and 2 c respectively. If A and B are given Q and 4Q amounts of heat respectively, the change in their temperatures is the same. If the mass of A is m, what is the mass of B?
Given : cA = c , cB = 2c, QA = Q, QB = 4Q ΔT= same, mA = m, mB = ? We know Q = mcΔT ∴ΔT = Q/mc As ΔT is same for substance A and B ∴ \(\frac{Q_A}{m_Ac_A}=\frac{Q_B}{m_Bc_B}\) ∴ \(\frac{Q}{mc}=\frac{4Q}{m_B2c}\) ∴ mB = 2m This is the mass of B
e. When a substance having mass 3 kg receives 600 cal of heat, its temperature increases by 10 0C. What is the specific heat of the substance?
Given : m = 3kg, = 3000 g, Q = 600 cal, ΔT = 10 0C, c = ? We know Q = mcΔT ∴ c = Q/mΔT = 600/(3000 x 10) = 0.02 cal/g 0C This is the specific heat of substance
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 13-Chemical Change and Chemical Bond - online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 15-Sound -online Solution |