Carbon: An Important Element
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-13
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
An Element : A substance which cannot be broken down into simple substances by any chemical reaction is called an element.
Types of elements : Metals, non-metals and metalloids are the different types of elements.
Carbon : Carbon is a non-metallic element.
- Carbon is the main constituent of all plant and animal products.
- In nature, it is found in the free state and also in compounds.
- On complete combustion of any organic compound, carbon dioxide and water are formed.
| 1. Symbol of carbon – C 2. Atomic number – 6
3. Atomic mass – 12 4. Electron configuration – 2,4 5. Valency – 4 6. Non-metallic element |
Compound : A substance produced by a chemical reaction of two or more elements is called a compound. Compounds are obtained directly or indirectly from plants or animals and compounds are also obtained from minerals.
Occurrence of carbon : In the free state, carbon is found as diamond and graphite. In the combined state, carbon is found in the following compounds :
- Carbon dioxide, calcium carbonate, marble and calamine (ZnCO3).
- Coal, petroleum and natural gas.
- Carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
- Natural fibres such as cotton, wool, silk.
In the earth’s crust, carbon is present to the extent of approximately 0.27% in the form of carbonate, coal and petroleum. The proportion of carbon in the form of carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere is approximately 0.03 %.
Allotropes of an element : Some elements are found in nature in more than one form. They have same chemical properties but different physical properties. These forms are called allotropes of an element.
Properties of Carbon : Carbon exhibits allotropy. It exists in more than one form. The chemical properties of these different forms are the same but their physical properties are different.
Carbon allotropes have two forms : crystalline form and amorphous form..
- Crystalline forms : (i) It has a regular and definite arrangement of atoms. (ii) They have high melting points and boiling points. (iii) A crystalline form has a definite geometrical shape, sharp edges and plane surfaces. (iv) Carbon has three crystalline allotropes : 1. Diamond 2. Graphite 3. Fullerene.
- N0n-crystalline/ Amorphous forms : The arrangement of carbon atoms is irregular. Examples : Coal, charcoal, coke.
Diamond : Diamonds are found in India in Govalkonda (Karnataka) and Panna (Madhya Pradesh). In diamond, each carbon atom is linked to four other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. Therefore, diamond has tetragonal three dimensional structure. It does not dissolve in any solvent. Diamond

Graphite : In the natural state, graphite is found in Russia, New Zealand, America and India.
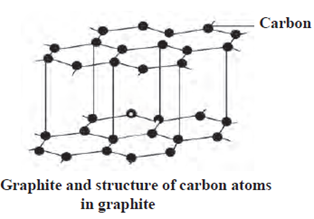
Fullerene : Fullerene, an allotrope of carbon, is rarely found in nature. C60, C70, C76, C82 and C86 are other examples of fullerene found in small numbers in soot.

Amorphous Forms of Carbon : The arrangement of carbon atoms in amorphous form is not regular. Coal, charcoal, coke are the non-cystalline forms of carbon.
| Fossil fuels :The fuels formed over millions of years by the burial of plants and animals are called fossil fuels. They contain energy rich carbon compounds originally made by plants. Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels. |
Q. How did coal form in nature?
Ans. Millions of years ago the remains of plants and animals got buried under the earth. Due to action of microorganisms, the gaseous substances in these remains were released into the atmosphere and the left behind was carbon compounds. After this, under tremendous pressure, the liquid substances in these compounds drained away and the remaining mineral solidified into compact and hard rock and this material is called coal.
Carbon dioxide : Molecular formula : CO2, Molecular mass 44.
Occurrence : Carbon dioxide occurs in free state in atmosphere to the extent of about 0.03 %. Exhaled air contains about 4% of CO2.
- It is found in chalk and shahabad tiles/marble/ limestone in compound form.
- In the combustion of wood and fossil fuel coal, CO2 is given out.
Physical Properties : Chemical properties :
Uses :
Hydrocarbons : Carbon and hydrogen are included in most organic compounds. These basic organic compounds are called hydrocarbons. The electronic configuration of carbon is 2,4, therefore, the valency of carbon is 4.
A carbon atom can form four covalent bonds with other carbon atoms or atoms of different elements.
Properties of covalent compounds:
Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbons : Carbon atom exhibits a characteristic property. They can form a chain of carbon atoms by forming covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. The hydrocarbons having only single bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated hydrocarbons.
Examples : Ethane (C2H6) which is (CH3—CH3), propane (CH2 — CH2 — CH3).
Some hydrocarbons have a multiple bond (a double bond or a triple bond) between two carbon atoms. Hydrocarbons having at least one multiple bond are called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Examples : Ethene (CH2 = CH2), ethyne (HC Ξ CH), propene (CH3—CH=CH2), propyne (CH3—C Ξ CH).
Methane : Molecular formula : CH4, Molecular mass 16.
Occurrence :
- Methane occurs in natural gas to the extent of 87%.
- The decomposition of vegetable matter in the absence of air produces methane.
- It is obtained from the biogas.
- It is found in coal mines.
- Methane is found at the surface of marshy places, therefore, it is also called marsh gas.
- In the laboratory, when a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide gases are heated at 300°C in the presence of nickel as a catalyst, methane gas is formed.
- Methane gas in pure form is obtained by fractional distillation of natural gas.
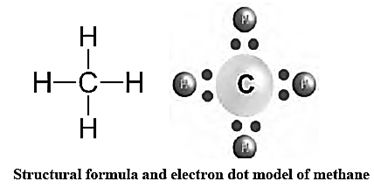
Physical properties of methane : Chemical properties of methane : Methane is highly inflammable. It burns by reacting with oxygen to give a bluish flame. In this reaction, 213 kcal/mol of heat is given out. Methane burns completely. Chemical reactions : CH4+2O2 -> CO2+ 2H2O + heat CH4+Cl2 -> CH3Cl +HCl
Uses of methane :
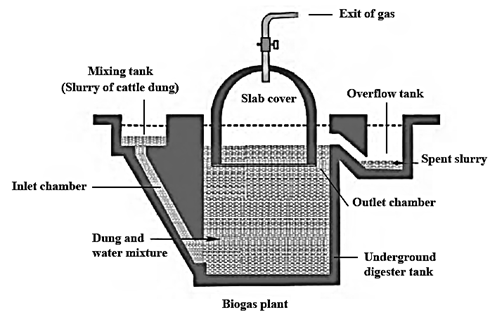
Biogas plant : In a biogas plant, animal dung, wet garbage is decomposed by anaerobic microbes. This produces methane gas and carbon dioxide and it is called biogas.
The production of biogas is an anaerobic process. It takes place in two stages.
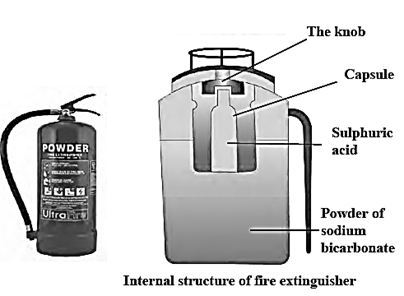
Fire extinguisher : Chemical reaction : 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 -> Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 12: Study of Sound - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 14: Substances in Common Use - online Notes |

It’s very important notes sir thanks for sharing this I understand now what is carbon and it’s compounds and
Its properties
Very important notes
Yah that’s true 👍
Aap bahut achcha banate Ho ISI tarah bnao mujhe aap project banana hai school mein to mujhe aap food chain bhej sakte hain maine vah sab