Life Processes in Living Organisms-2
Based on Class 10-Science & Technology Part-2-Chapter-3- Maharashtra Board-Audio Notes, Solution, Videos, PDF
Solution
Question 1:
Complete the following chart.
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction | ||
| 1. | Reproduction that occurs with the help of somatic cells is called as asexual reproduction. | 1. | ---- |
| 2. | ------ | 2. | Male and female parent are necessary for sexual reproduction. |
| 3. | This reproduction occurs with the help of mitosis only. | 3. | ------ |
| 4. | ----- | 4. | New individual formed by this method is genetically different from parents. |
| 5. | Asexual reproduction occurs in different individuals by various methods like binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation, spore production, etc. | 5. | ------- |
Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
1.
Reproduction that occurs with the help of somatic cells is called as asexual reproduction.
1.
Reproduction that occurs with the help of germ cells is called sexual reproduction.
2.
Both the parents are not required for asexual reproduction. It is uniparental
reproduction.2.
Male and female parent are necessary for sexual reproduction.
3.
This reproduction occurs with the help of mitosis only.
3.
This reproduction occurs with the help of both meiosis and mitosis.
4.
New individual formed by this method is genetically identical to parents.
4.
New individual formed by this method is genetically different from parents.
5.
Asexual reproduction occurs in different individuals by various methods like binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation, spore production, etc.
5.
Sexual reproduction occurs in various organisms like microbes, plants, animals and humans. It involves two main processes- gamete formation and fertilization.
Question 2:
Fill in the blanks.
a. In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ ----------------.
b. In humans, ------ chromosome is responsible for maleness.
c. In male and female reproductive system of human, ------------- gland is same.
d. Implantation of embryo occurs in ------
e. ---------- type of reproduction occurs without fusion of gametes.
f. Body breaks up into several fragments and each fragment starts to live as a new individual. This is -- -- -- -- -- -- -- type of reproduction.
g. Pollen grains are formed by -- ----- -- -- -- division in locules of anthers.
a. In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ testes.
b. In humans, Y chromosome is responsible for maleness.
c. In male and female reproductive system of human, bulbourethral gland is same.
d. Implantation of embryo occurs in uterus.
e. Asexual type of reproduction occurs without fusion of gametes.
f. Body breaks up into several fragments and each fragment starts to live as a new individual. This is fragmentation type of reproduction.
g. Pollen grains are formed by meiotic division in locules of anthers.
Question 3:
Complete the paragraph with the help of words given in the bracket.
(Luteinizing hormone, endometrium of uterus, follicle stimulating hormone, estrogen, progesterone, corpus luteum)
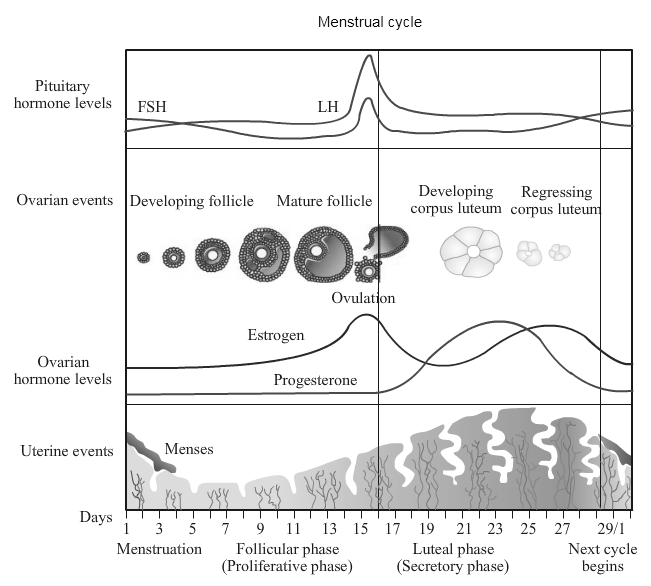
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of ----- This follicle secretes estrogen. -- --- - -- -- -- grows / regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of --- ---, fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and -- --- -- -- is formed from remaining part of follicle. It secrets --- --- -- -- and --- --- -- -- --. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of -- -- -- -- are activated and it becomes ready for implantation.
Growth of follicles present in the ovary occurs under the effect of follicle stimulating hormone. This follicle secretes estrogen. Endometrium of uterus grows/regenerates under the effect of estrogen. Under the effect of luteinizing hormone, fully grown up follicle bursts, ovulation occurs and corpus luteum is formed from remaining part of follicle. It secretes progesterone and estrogen. Under the effect of these hormones, glands of endometrium of uterus are activated and it becomes ready for implantation.
Question 4:
Answer the following questions in short. Asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms can be of three types: 1. Binary fission : 2. Organisms : (1) Simple: Bacteria and Amoeba. (2) Transverse : Paramoecia. (3) Longitudinal : Euglena and eukaryotic cell-organelle like mitochondria and chloroplasts 3. Multiple Fission : Organisms : Amoeba in unfavourable conditions. Budding : Organisms : Yeast cells (Unicellular fungus)
1. Explain with examples types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organism.
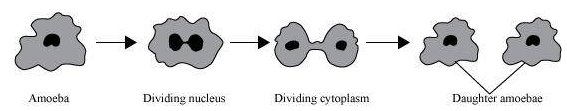
2. Explain the concept of IVF.
Many couples all over the world who are unable to produce children due to various reasons. These couples can be assisted to have children through techniques called assisted reproductive technologies (ART). IVF is one such form of ART which includes different methods that can be a boon for childless couples: In Vitro Fertilization : If Less sperm counts in Man or obstacles in oviduct of woman then fertilization is done in a test-tube .The embryo formed is implanted in uterus of woman. Surrogacy- This is a technique which is used for women who face problem in implantation of embryo in uterus. In this technique the donor of the oocyte is the women itself who has problem in implanting the embryo in the uterus. The collected oocyte is fertilized with the sperm of her husband in a test tube. The embryo which is obtained after fertilization is implanted in the uterus of another female who is called the surrogate mother. ZIFT − It stands for zygote intra fallopian transfer. In ZIFT, the sperm from a donor male and the ova from a donor female are fused in the laboratory. The zygote so formed is transferred into the fallopian tube at the 8 blastomeres stage. IUT − It stands for intra uterine transfer. In this technique, embryos with more than 8 blastomeres are transferred into the uterus.
GIFT − It stands for gamete intra fallopian transfer. In GIFT, females who cannot produce ovum, but can provide suitable conditions for the fertilisation of ovum, are provided with ovum from a donor.
ICSI − It is a intra cytoplasmic sperm injection. In this method, sperm is directly injected into the cytoplasm of the ovum.
Artificial insemination − In this technique, the semen collected from the husband or a donor is injected into the vagina or uterus. This cures the infertility arising from the inability of the male partner to ejaculate, or due to low sperm count.
3. Which precautions will you follow to maintain the reproductive health?
4. What is menstrual cycle? Describe it in brief.
Menstrual cycle is the reproductive cycle in all primates and begins at puberty (menarche).
Question 6:
Sketch the labeled diagrams:
1. Human male reproductive system

2. Human female reproductive system
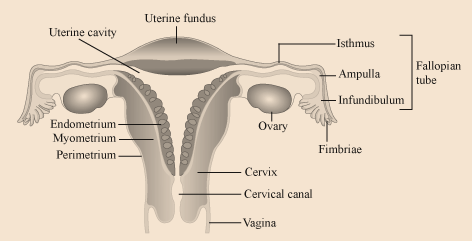
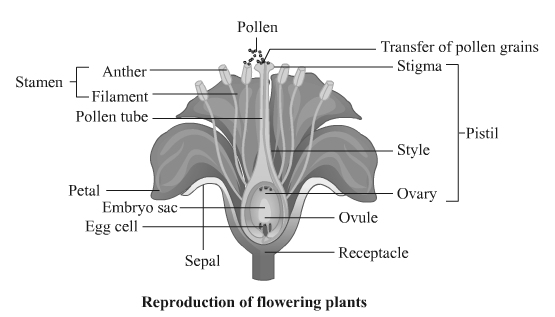
3. Flower with its sexual reproductive organs
4. Menstrual cycle
Question 7:
Give the names.
a. Hormones related with male reproductive system.
b. Hormones secreted by ovary of female reproductive system.
c. Types of twins.
d. Any two sexual diseases.
e. Methods of family planning.
a. Hormones related with male reproductive system- Testosterone, Follicle stimulating hormone, ICSH or Luteinizing hormone
b. Hormones secreted by ovary of female reproductive system- Estrogen and Progesterone
c. Types of twins- Monozygotic, Siamese and Dizygotic twins
d. Any two sexual diseases- AIDS, Syphilis and Gonorrhea
e. Methods of family planning- Oral pills, condoms, IUD's, Copper T
Question 8:
Gender of child is determined by the male partner of couple. Explain with reasons whether this statement is true or false.
The statement Gender of child is determined by the male partner of couple is true Human females have two X chromosomes (XX) and human males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Therefore, the eggs produced by females have only X chromosomes while the sperms produced by males can have either X or Y chromosome. If an unfertilised egg fuses with a sperm containing X chromosome, then it gives rise to a girl child having two X chromosomes. If an unfertilised egg fuses with a sperm containing Y chromosome, then it gives rise to a male child having one X and one Y chromosome.
Question 9:
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
1) Vegetative propagation is the method of asexual reproduction in plants. This form of asexual reproduction occurs in plants only. In vegetative propagation, parts of old plant like stems, roots and leaves are used to grow a new plant. The buds which are present in dormant state in old plant are provided with suitable conditions like moisture and warmth so that they grow and develop to form a new plant. Plants that undergo vegetative propagation are green grass, Bryophyllum, money plant, potato plant, onion, banana, etc. (1) It takes place with the help of vegetative parts like root, stem, leaf and bud. The various methods of vegetative propagation are: From underground stem: A potato plant has an underground stem known as the tuber. It has many buds called eyes. A vegetative bud consists of a short stem, around which immature overlapping leaves are present in a folded state. A bud can give rise to a new plant through asexual reproduction. Rhizome: The underground stem of ginger is known as the rhizome which is capable of giving rise to a new plant. Corm is the underground stem as found in Gladiolus. It can also be used for vegetative propagation. Through leaves: Leaves perform the function of photosynthesis. However, they can take part in asexual reproduction as well. In some plants, leaves can give rise to a new plant asexually. For example, the leaves of the plant Bryophyllum contain buds on its margins. These buds give rise to a new plant through asexual reproduction. From aerial stem: In certain plants, a slender stem arises from the base of the plant and touches the soil, it develops roots and buds at the point of contact with the soil and gives rise to new plants. When the new plant is old enough the stem connecting it to the parent plant withers away.
(2) Carrot, beet root and radish are the modified roots that perform vegetative propagation.
(3) Potato, suran (Amorphophallus) and other tubes propagate with the help of 'eyes' which are buds. These eyes are present on the stem tubers.
(4) In case of plants like sugarcane & grasses, buds present on nodes perform vegetative propagation.
(5) Plants like Bryophyllum performs vegetative propagation with the help of buds present on leaf margin.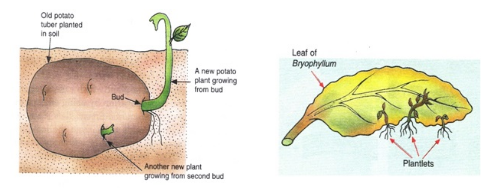
Question 10:
Modern techniques like surrogate mother, sperm bank and IVF technique will help the human beings. Justify this statement.
(1) Some couples want a child but they are not able to bear one due to various problems either in mother or in father In such cases modern techniques such as IVE, surrogacy and sperm bank are useful in conceiving a child. (2) In woman if there are problems like irregularity in menstrual cycle, difficulties in oocyte production or implantation in uterus, obstacles in the oviduct, etc. then she can resort to any one technique of the above. (3) In man if there are ho sperms in the semen. slow movement of sperms, or anomalies in the sperms then he becomes sterile (4) But now with the help of advanced medical techniques these problems can be overcome and a childless couple can be parents (5) These methods are as follows :
Question 11:
Explain sexual reproduction in plants.

Click on below link to get PDF from store
Class 10-Science & Technology-2-Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2-Notes
Class 10-Science & Technology-2-Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2-Solutions
Class 10-Science & Technology-2-Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2-Books
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Class 10-Sc. & Tech-2-Chapter-2-Life Processes in Living Organisms-1 - Online Notes Next Chapter : Class 10-Sc. & Tech.-2-Chapter-4-Environmental management - Online Notes |
