Inside the Atom
Based on Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter 5-Notes-Solutions-Videos-Tests-PDF
Solution
Question 1:
Answer the following
1. What is the difference in the atomic models of Thomson and Rutherford ?
Difference between Thomson and Rutherford Theory are as follows :
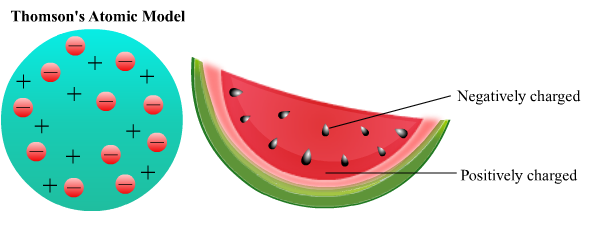
Thomson’s atomic model
Rutherford’s atomic model
According to Thomson’s atomic model negatively charged electron are embedded in a gel of positively charge.
According to Rutherford’s atomic model the negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus
Does not give any detail about the atomic nucleus
Explains about the atomic nucleus
States that electrons are uniformally distributed in an atom
States that electrons are located around a central solid material
Indicates that atom is spherical in shape
Indicates that an atom has a central solid core called as nucleus surrounded by the electrons
Does not give any idea about constituents of nucleus
States that nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons
2. What is meant by valency of an element ? what is the relationship between the number of valence electron and valency ?
Valency of an element : It is the number of electrons of an atom of the element uses to combine with atoms of other elements. It is the combining power of an atom of the element. It gives idea about the number of electrons loss or gain in order to achieve the nearest noble gas configuration. Number of valence electron : It is defined as the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. It means that there is relationship between the valency of an element and the number of electrons in its valence shell.
For example: Na(11) = 2,8,1 So, its valency is 1
Cl(17) = 2,8,7 So, its valency is also 1
3. What is meant by atomic mass number ? Explain how the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
Atomic Mass Number : The total number of protons and neutrons present in a nucleus of the atom is called atomic mass number. Atomic number of Carbon atom (Z) = number of protons = number of electrons = 6.
Atomic mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons.
Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons. It is denoted by Z.
Mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons. It is denoted by A.
For Carbon atom - Number of proton = 6, Number of neutrons = 6, Number of electron = 6
Atomic Mass number of Carbon atom (A) = number of proton + number of neutrons = 6 + 6 =12.
4. what is meant by subatomic particle ? give brief information of three subatomic particles with reference to electrical charge, mass and location.
Subatomic particles : A particle which is a constituent of an atom hence smaller than the atom is called subatomic particle. Electron : Proton : Neutron :
1. Electrons are present outside the nucleus of an atom.
2. Electrons are negatively charged that is (1.6 × 10−19 coulomb).
3. The mass of an electron is considered to negligible. It is 1800 times less than that of a hydrogen
4. It revolves around the nucleus in the discrete orbit.
1. Protons are present in the nucleus of an atom.
2. Protons are positively charged that is (1.6 × 10−19 coulomb).
3. The mass of a proton is approximately 1u(1Dalton) that is (1u = 1.66 × 10−27 g).
4. They are closely bound in the nucleus.
1. Neutrons are present in the nucleus of an atom.
2. Neutrons are neutral. There is no charge.
3. The mass of a neutron is nearly equal to the mass of a proton that is 1u(1Dalton) that is (1u = 1.66 × 10−27 g).
4. They are closely bound in the nucleus.
Question 2:
Give scientific reasons.
1. All the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
All the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus because atom contains three subatomic particles like electron, proton and neutron. Out of which, nucleus present at the centre of an atom contains two subatomic particles that's protons and neutrons and the mass of nucleus is the sum of mass of protons and neutrons located at the centre of an atom.
2. Atom is electrically neutral.
Atom is electrically neutral because in an atom electrons and protons carry charges and each atom has equal numbers of protons (positively charged) and electrons (negatively charged).
3. Atomic mass number is a whole number.
Atomic mass number is a whole number because it is the sum of numbers of protons and numbers of neutrons present in an atom. Which is present in the form of integers.
4. Atoms are stable though negatively charged electron are revolving within it.
Atoms are stables though negatively charged electrons are revolving within it because each atom contains equal numbers of protons and electrons. So, charge on negatively charged electrons are balanced by charge on positively charged proton. Therefore, atom is electrically neutral and stable.
Question 3:
Define the following forms
A. Atom
Atom: An atom is the smallest particle of an element which retains its chemical identity in all physical and chemical changes.
Because atoms are the smallest things in the universe and could not be divided. atoms are made up of three subatomic particles like protons, neutrons and electrons.
B. Isotope
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have same atomic number but different mass number. Isotopes have same numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
C. Atomic number
Atomic number (Z) : The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number. It is denoted by Z. Example :
Atomic number determines its place in the periodic table.
Atomic number of carbon = 6
Atomic number of nitrogen = 7
D. Atomic mass number
Atomic mass number (A) : The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number. It is denoted by A.
Atomic mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons.
E. Moderator in nuclear reactor
Moderator in nuclear reactor: Moderator of a nuclear reactor is a substance that slows down the speed of neutrons in a fission .
Question 4:
Draw a neat lablled diagram
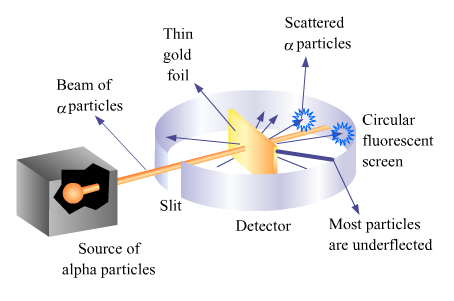
1. Ruthrford's scattering experiment
Rutherford's scattering experiment :
2. Thomson's atomic model
3. Diagramatic sketch of electronic configurations of magnesium (Atomic number 12)

4. Diagramatic sketeh of electronic configuration of Argon (Atomic number 18)

Question 5:
Fill in the blanks.
A. Electron, proton, neutron are the types of _________ in an atom.
B. An electron carries a _________charge.
C. The electron shell _____________ is nearest to the nucleus.
D. The electronic configuration magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this it is understood that the valence shell of magnesium is_____________
E. The valency of hydrogen is 'one as per the molecular formula H2O . Therefore valency of 'Fe' turns out to be ______________ as per the formula Fe2O3.
A. Electron, proton, neutron are the types of subatomic particlesin an atom. B. An electron carries a negativecharge. C. The electron shell K is nearest to the nucleus. D. The electronic configuration magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this it is understood that the valence shell of magnesium is M shell. E. The valency of hydrogen is 'one as per the molecular formula H2O . Therefore valency of 'Fe' turns out to be three as per the formula Fe2O3.
Question 6:
Match the pairs.
| Group 'A' | Group 'B' |
| a. Proton | 1. Negatively charged |
| b.Electron | 2.Neutral |
| c.Neutron | 3.Positively charged |
Match the pairs:
Group 'A'
Group 'B'
a.Proton
3.Positively charged
b.Electron
1.Negatively charged
c.Neutron
2.Neutral
Question 7:
Deduced from the datum provided.
| Datum | To deduce |
| \({^{23}_{11}Na}\) | Neutron number |
| \({^{14}_{6}C}\) | Mass number |
| \({^{37}_{17}Cl}\) | Proton number |
Datum
To deduce
\({^{23}_{11}Na}\)
Neutron number = Mass number - Number of protons
= 23 − 11
= 12
\({^{14}_{6}C}\)
Mass number = 14
\({^{37}_{17}Cl}\)
Proton number = Atomic number = 17
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : MSBSHSE -Class 8th Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Previous Chapter : Chapter 4: Current Electricity and Magnetism - view online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 6- Composition of Matter-view online Solution |
Excellent the answers are fully correct keep it up