Trade
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Geography-Chapter-9
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
The concept of trade :
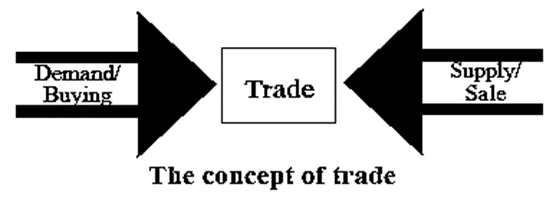
- We have various needs in our day-to-day life. We buy various things to satisfy these wants. When we buy them, we create a demand for them.
- Production of these goods is carried out to fulfil the demand. The producers supply these goods.
- Buying and selling of goods is done to fulfil each other’s needs. Those who purchase are the consumers of the goods. The producer produces and the sellers sell the goods. This activity of buying and selling goods is called trade.
Trade is an age-old concept :
Importance of Trade :
- Trade is an important economic activity because the economic life of people is interdependent. No region or country is self-sufficient.
- The region or country which has goods in excess, supplies these goods/commodities to those regions or countries which are deficit as per their demand.
- Buying and selling of goods, is called visible trade. An exchange of services is called invisible trade.
- Thus, trade sustains the economy not only of one country but the world at large.
Types of Trade:
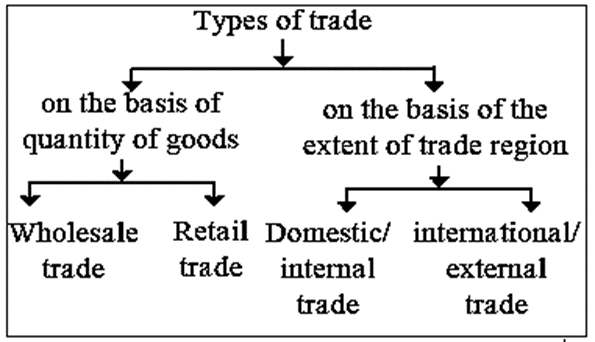
On the basis of the Quantity of Trade : The following are two types of trade on the basis of quantity of trade : (i) Wholesale Trade : (ii) Retail Trade :
On the basis of the Extent of Trade: The following are two types of trade on the basis of the extent of trade : (i) Domestic/Internal Trade : (ii) International/External Trade:
Import and Export :
- Import and export are the basic processes of international trade.
(i) Import :
- Import is buying of the commodities, goods and services that are scarce in the country from the other country.
- When the value of the imported goods is more than the value of the exported goods, there is adverse balance of trade.
- Adverse balance of trade has negative impact on the economy of the country
(ii) Export :
- Export is selling of excess goods and services to countries which have a demand for it.
- When the value of the exported goods is more than the value of the imported goods there is favourable balance of trade.
- Favourable balance of trade has positive impact on the economy of the country.
Balance of Trade :
The difference between the value of imports and the value of exports in a specific period is called balance of trade.
- Unfavourable balance of trade arises when the value of imports is more than the value of exports.
- Favourable balance of trade takes place when the value of exports is more than the value of imports.
- When there is not much difference in the value of exports and imports it is called Balance of Trade.
International Trade Organisations :
International trade is more complex than domestic trade due to :
- Differences in the nature of economy;
- Differences in the policies of the government;
- Differences in market, laws, judicial system, currency, language, etc.
Factors like the economy of the country, government policies, markets, laws, judicial system, currency, language, etc. influence the trade.
To avoid the differences and obstacles between the countries, International economic and trade organisations were established.
They smoothen and promote international trade. They facilitate the growth of international trade.
The details of a few organisations have been given here in the following :
(1) World Trade Organisation (WTO) : Aims/functions : (2) European Union (EU): European Common Market was established in 1964 and it gradually evolved into European Union of 28 countries in Europe. Aims/functions : (3) Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC): Aims/functions : (4) South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC): (SAARC) is the regional organization of the countries in the South Asia. India is a member of the SAARC. Aims/functions : (5) Association of South-East Asian nations (ASEAN): Aims/functions : (6) Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC): Aims/functions : (7) Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (BRICS): Aims/functions : Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa have formed BRICS for mutual cooperation. The objectives of the BRICS are as follows :







Marketing :
- Marketing is an invisible flow of the activities that begins with the production of goods and ends with the product reaching the consumers.
- The activities involved are : (i) Production (ii) Classification (iii) Branding (iv) Labelling and (v) Packaging
- Thereafter, pricing, sales promotion and distribution of goods takes place.
Importance of Marketing :
Advertisement :
- Advertising is a part of the sales promotion activity. It attracts the customers to buy the goods.
- The objectives of advertisements are to reach maximum customers, attract them to the products and make them buy the products.
- Products loose their credibility and trust of customers when the manufacturers and Sellers indulge in unfair practices.
- Giving incomplete or incorrect information exaggerated statements and pointing out the shortcomings of the other products result in lost of trust.
- Therefore, it is necessary that the manufacturers, follow fair (ethical) practices in advertising, follow rules and regulation laid down in Consumer Protection Act.
- It is also important that the consumer identifies his needs and buys goods at reasonable rates.
Click on link to get PDF from store :
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 8: Introduction to Economics - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 10: Urbanisation - online Notes |